The Intricate Journey of Water: From Your Kitchen Sink to the Sewer System
Introduction
Every day, as we rinse dishes or pour liquids down our kitchen sinks, we seldom pause to consider the remarkable journey that water undertakes once it vanishes down the drain. This journey is not just a marvel of modern plumbing but also a testament to our society's efforts in maintaining environmental health.
The Starting Point - Anatomy of a Kitchen Sink
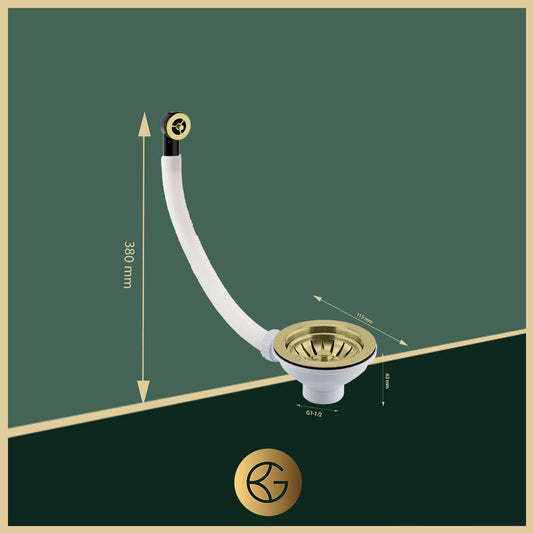
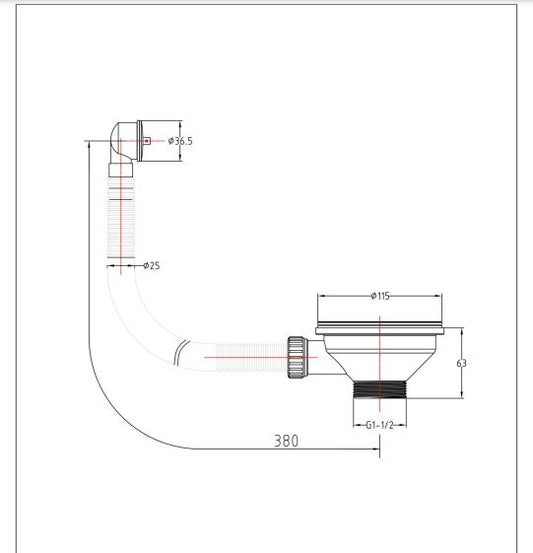
Our exploration begins with the kitchen sink, a common household fixture yet a complex assembly. It comprises a faucet, basin, and a crucial component hidden from view - the drain.
The drain is equipped with a P-trap, an ingeniously designed curve in the piping that holds a water seal to prevent unpleasant sewer gases from entering our homes. The design and material of the sink, ranging from stainless steel to ceramic, play a vital role in its functionality and durability.
The Hidden Pathways - Understanding Drain Pipes
Beneath the sink lies a network of pipes, often unseen and unthought-of. These pipes, crafted from various materials like PVC or copper, are meticulously sloped to utilize gravity in guiding wastewater away from our homes. The evolution of these materials over time reflects advancements in plumbing technology and environmental considerations.
Breathing Easy - The Role of Ventilation in Plumbing
Integral to this system is the plumbing ventilation - a setup that prevents vacuums in the drain pipes, ensuring a smooth, uninterrupted flow of water. Ventilation pipes extend from the drainage system up through the roof, balancing air pressure and preventing potential backflow issues that could disrupt the drainage.
Joining the Larger Network - Connection to Main Sewer Lines
From individual homes, these networks of pipes converge into a larger, communal sewer system or, in some rural areas, into septic systems. These connections, established during the construction of a house, dictate the path of wastewater from our homes to either a municipal treatment facility or a self-contained septic tank.
The Community's Role - Municipal Sewer Systems
In urban areas, the municipal sewer system takes the baton. Here, the labyrinth of underground pipes channels the collective wastewater to treatment plants. These facilities employ a series of advanced processes like sedimentation, biological treatment, and disinfection to purify the water, thus playing a crucial role in preserving public health and environmental quality.
Self-Contained Solutions - Septic Systems Explained
For homes with septic systems, the process is more localized but equally sophisticated. These systems separate solids and liquids in the tank, with the liquid effluent eventually percolating into the surrounding soil in the drain field. This natural filtration process is pivotal in areas without access to municipal sewer systems, though it demands regular maintenance and a keen awareness of what goes down our drains.
Environmental Awareness and Your Kitchen Sink
This brings us to an essential aspect of our journey - environmental awareness. The path from sink to sewer is not just a journey of water but also of everything we dispose of down our drains.
Harsh chemicals, oils, and non-biodegradable substances can wreak havoc on plumbing systems and local ecosystems alike. Adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using safe cleaning agents and proper disposal methods, is not just beneficial for our plumbing but imperative for our environment.
Conclusion
In summarizing, the journey of water from our kitchen sinks to the sewer or septic system is a complex yet fascinating process.
It underscores the importance of understanding and responsibly managing our household systems, not only for efficient home maintenance but also for the greater good of environmental stewardship.
As we go about our daily routines, a mindful approach to what we let go down our drains can make a significant difference in the health of our planet.
explore our kitchen sink wastes collection here
other related blogs: