Choosing the Right Radiator for Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide
Table Of Contents:
-
Introduction
→ -
Traditional Towel Rails Collection
→ -
Understanding Radiators and Their Functionality
→ -
Types of Radiators
→ -
How to Choose the Perfect Radiator for Your Home
→ -
Exploring Radiator Styles: Choosing the Perfect Fit for Your Home
→ -
Radiator Materials: Selecting the Right Material for Optimal Heating and Style
→ -
Installing a Radiator: A Step-by-Step Guide
→ -
Maintaining and Cleaning a Radiator: Tips for Long-Lasting Efficiency
→ -
Cost of Radiator Maintenance in the UK
→ -
BTU Ratings: Understanding Heat Output
→ -
Energy Consumption by Radiators in the UK
→ -
Radiator Valves: Essential Components for Efficient Heating
→ -
Essential Accessories and Considerations for Radiator Installation and Maintenance
→ -
Buying Tips for Choosing the Right Radiator
→ -
Conclusion
→ -
Frequently Asked Questions
→
Introduction
When it comes to heating your home, selecting the right radiator is just as important as picking the right heating system. A radiator not only keeps your living space warm but also contributes to the overall aesthetics of your room. With so many options available, choosing the right radiator might feel overwhelming. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the key factors to consider when choosing a radiator for your home, including different types, materials, installation tips, and more.
Understanding Radiators and Their Functionality
A radiator is an essential component of any home’s heating system, responsible for distributing warmth throughout your living spaces. While radiators have been around for centuries, they have undergone significant changes in design and efficiency. Whether you're replacing an old radiator or installing a new one, understanding how radiators work and their key features can help you make the right choice for your home.

At its core, a radiator functions as a heat exchanger. It receives heat from hot water or steam circulating through pipes connected to a central heating system and transfers that heat to the air in the room, warming up the space. This process is a combination of convection (the movement of warm air) and radiation (heat emitted directly from the radiator surface).
Here’s how it works:
-
Hot Water or Steam Circulation: Radiators are connected to a central heating system where hot water (in a wet heating system) or steam (in a steam heating system) is pumped into the radiator.
-
Heat Transfer: Once the hot water or steam enters the radiator, it warms the metal surface of the radiator. The metal then radiates heat into the room, warming the surrounding air.
-
Air Circulation: As the air near the radiator heats up, it becomes less dense and rises. This warm air moves around the room, cooling down as it spreads, while cooler air is drawn in to replace it, creating a natural convection cycle.
-
Heat Loss: The radiator continues to emit heat until the room reaches the desired temperature, and the heating system turns off.
In addition to its primary role of providing heat, modern radiators come in various styles and materials that can complement the design of your home. Whether you’re installing a traditional cast iron radiator or opting for a sleek, modern panel radiator, choosing the right one can make a difference in both your home’s comfort and aesthetic appeal.
Radiator Efficiency and Performance
The efficiency of a radiator largely depends on the material it is made from, its size, and its heat output (measured in BTUs – British Thermal Units). A larger radiator or one with a higher BTU rating is better suited for larger rooms or spaces that require more heat. Radiators made from materials like cast iron or aluminum are known for their heat retention properties, while steel radiators typically heat up quickly and are ideal for smaller spaces or rooms that require fast heating.
As energy costs continue to rise, selecting the right radiator can also help reduce heating costs. High-efficiency radiators, like those with thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs), can help maintain a steady temperature without wasting energy.

Types of Radiators
Radiators come in a variety of styles and designs, each offering unique benefits and suited to different types of heating systems and home decor. Understanding the different types of radiators available is crucial when choosing the right one for your home. Below are the most common types of radiators used in residential settings:
1. Panel Radiators
Panel radiators are one of the most popular types of radiators. They are flat, compact, and feature a sleek design that suits modern and minimalist interiors. These radiators consist of one or two panels (hence the name) that heat up quickly and efficiently.
-
Best for: Modern, minimalist spaces with limited wall space.
-
Pros: Space-saving, quick to heat up, and energy-efficient.
-
Cons: They can lack character compared to traditional radiators.
2. Column Radiators
Column radiators have a more traditional and vintage aesthetic. They consist of vertical columns or sections and are available in both classic and contemporary designs. Cast iron column radiators are often used in period properties for a more authentic vintage look, while modern versions made from steel provide the same column structure but with more contemporary finishes.
-
Best for: Traditional, rustic, or industrial-style homes.
-
Pros: Large heat output, highly durable, and ideal for maintaining warmth in large spaces.
-
Cons: Can take longer to heat up compared to panel radiators.
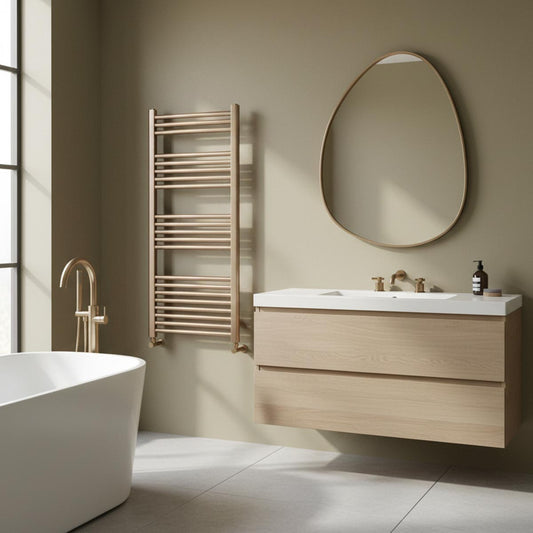
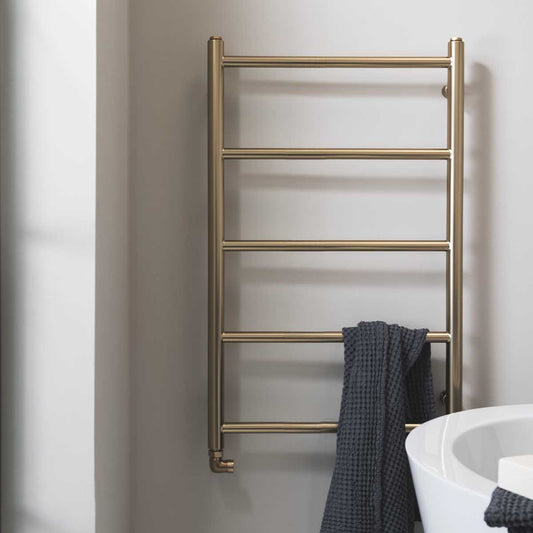
3. Towel Radiators
Towel radiators, also known as towel warmers, are designed to heat your bathroom while providing a place to hang towels. These radiators have horizontal bars that not only warm the air in the room but also dry your towels, keeping them toasty and free of moisture.
-
Best for: Bathrooms, kitchens, or small spaces that require heating and towel drying.
-
Pros: Multifunctional (heats and dries towels), compact design.
-
Cons: May not provide as much heat as larger radiators for larger rooms.
4. Electric Radiators
Electric radiators are standalone units that don't require any connection to a central heating system. Instead, they operate entirely on electricity, heating the room through electric coils or oil-filled reservoirs. These are ideal for spaces that don’t have a central heating system.
-
Best for: Rooms without central heating, or as supplementary heating in smaller spaces.
-
Pros: Easy to install, no need for a central heating system, portable.
-
Cons: Can be less energy-efficient than water-based radiators, depending on usage.
5. Aluminum Radiators
Aluminum radiators are a lightweight and energy-efficient option for heating systems. They heat up quickly and cool down just as fast. These radiators are ideal for smaller rooms or spaces where rapid heating is needed.
-
Best for: Smaller rooms, modern homes, or homes with a highly efficient heating system.
-
Pros: Lightweight, quick to heat up and cool down, energy-efficient.
-
Cons: May not provide enough heat for larger spaces.
6. Cast Iron Radiators
Cast iron radiators have a vintage appeal, often found in period properties or homes seeking a classic look. These heavy-duty radiators are known for their durability and ability to retain heat for long periods. While they take longer to heat up compared to other types, they provide lasting warmth even after the heating system is turned off.
-
Best for: Traditional and period-style homes.
-
Pros: Long-lasting, retains heat for a long time, classic aesthetic.
-
Cons: Slow to heat up, heavy, and can be more expensive.
7. Designer Radiators
Designer radiators come in a variety of unique, contemporary designs and offer both style and functionality. They are available in an array of materials, shapes, and finishes, allowing you to integrate a radiator as a stylish feature of your room.
-
Best for: Homes with contemporary or artistic decor, where the radiator is a focal point.
-
Pros: Highly customizable, available in a range of designs, finishes, and sizes.
-
Cons: Can be more expensive than standard radiators.
8. Underfloor Heating
Although technically not a radiator in the traditional sense, underfloor heating systems have become increasingly popular as a modern alternative to wall-mounted radiators. Underfloor heating involves installing heating pipes or electric cables under the floor, radiating warmth directly from the floor upwards.
-
Best for: New builds, bathrooms, and rooms with limited wall space.
-
Pros: Even heat distribution, frees up wall space, unobtrusive.
-
Cons: Higher installation cost, not suitable for retrofitting in existing buildings without significant renovation.
The type of radiator you choose will depend on your home's heating system, the size of the space, your aesthetic preferences, and your heating needs. From traditional column radiators to modern electric versions, each has its benefits and drawbacks. By carefully considering the layout and style of your room, as well as your desired level of comfort, you can select the right radiator to keep your space warm and stylish.

How to Choose the Perfect Radiator for Your Home
Choosing the right radiator is an essential part of creating a comfortable and energy-efficient home. With so many types, sizes, and styles available, it can be overwhelming to make the right decision. The radiator you select will impact both the overall heating efficiency of your home and its aesthetic. To help you make the best choice, here are some important factors to consider when selecting the right radiator for your space:
1. Room Size and Heat Output
The size of your room plays a major role in determining the type and size of radiator you need. Larger rooms require radiators with a higher heat output, while smaller rooms can be adequately heated with smaller units. The heat output of a radiator is measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units). To ensure your room is properly heated, it's crucial to match the radiator’s BTU rating with the room's size.
-
Small rooms (e.g., bathrooms, kitchens): A compact radiator with a lower BTU rating is sufficient.
-
Medium rooms (e.g., bedrooms, offices): A medium-sized radiator with a moderate BTU output should work.
-
Large rooms (e.g., living rooms, open-plan areas): A larger radiator with a higher BTU rating is necessary to ensure efficient heating.
2. Radiator Type
As previously mentioned, radiators come in a variety of types, such as panel radiators, column radiators, electric radiators, towel warmers, and more. The type of radiator you choose will depend on your space, design preferences, and heating needs.
-
Panel radiators: Best for modern, minimalist spaces where functionality is key.
-
Column radiators: Ideal for traditional or industrial-style interiors.
-
Electric radiators: Perfect for homes without central heating or for supplementing existing systems in specific rooms.
-
Towel radiators: Best for bathrooms, where you need a combination of heating and towel drying.
3. Radiator Material
The material of a radiator determines how well it conducts and retains heat. Common radiator materials include:
-
Steel: Lightweight, quick to heat up, and widely available. Steel radiators are often more affordable and are available in a range of styles.
-
Aluminum: Known for its quick heat-up time and energy efficiency, aluminum radiators are often used in modern designs.
-
Cast iron: Classic and durable, cast iron radiators retain heat for a long time and provide excellent heating in larger rooms, although they take longer to heat up initially.
4. Style and Aesthetic
Your radiator should complement the overall design of your room. Whether you prefer traditional elegance or contemporary minimalism, there are radiators available in a range of styles:
-
Traditional styles: Cast iron column radiators or classic designs that complement period homes.
-
Modern styles: Sleek, slimline panel radiators or designer radiators that add a stylish touch to contemporary interiors.
-
Decorative options: Radiators come in various colors, finishes (such as matte, gloss, or brushed), and shapes to match your room’s decor. Designer radiators offer an opportunity to incorporate a radiator as a statement piece.
5. Energy Efficiency
Choosing an energy-efficient radiator will not only save on heating bills but also contribute to a more sustainable home. Radiators that are compatible with modern heating systems, such as condensing boilers or heat pumps, are more energy-efficient. Additionally, the material of the radiator affects its efficiency. Aluminum, for example, heats up quickly and uses less energy to maintain heat compared to other materials like cast iron.
6. Installation Considerations
The installation process for radiators varies depending on the type and location of the radiator. If you're replacing an existing radiator, installation may be relatively simple. However, if you're opting for an underfloor heating system or a radiator with complex features, it may require more effort and professional assistance.
-
Wall-mounted radiators: These are typically easier to install and work well for most rooms.
-
Freestanding radiators: Can be placed anywhere in the room but may take up more space.
-
Underfloor heating: Best for new builds or complete renovations, as it requires installation beneath the floor.
7. Budget
Radiators are available at a range of price points, from budget-friendly options to high-end designer radiators. Your budget will influence the material, size, and style of the radiator you choose.
-
Affordable radiators: Steel panel radiators and aluminum options are generally the most cost-effective.
-
Mid-range radiators: Cast iron radiators and more designer-friendly options typically fall into this category.
-
High-end radiators: Designer radiators, high-efficiency models, or custom finishes will cost more.
8. Radiator Valves
Don’t forget the importance of radiator valves, as they allow you to control the flow of water and adjust the temperature of the radiator. There are different types of valves to consider, including:
-
Manual valves: Allow for basic control of heat output.
-
Thermostatic valves: Automatically adjust the flow of water to maintain a set temperature, improving energy efficiency.
-
Angle valves: Used to connect radiators to pipes at a 90-degree angle.
9. Space and Positioning
Consider the available wall space in your room and the radiator’s position. A radiator placed beneath a window can help counteract drafts, while positioning it away from furniture will ensure optimal heat distribution. Additionally, consider how the radiator will affect the flow of space and your room’s overall design.
Choosing the right radiator for your home involves evaluating several factors, including room size, heating needs, style preferences, and material options. Taking the time to research the different types of radiators available will help you make an informed decision that suits both your heating requirements and aesthetic vision. By keeping these considerations in mind, you’ll find a radiator that provides efficient warmth, complements your space, and enhances the comfort of your home.
Exploring Radiator Styles: Choosing the Perfect Fit for Your Home
When selecting a radiator, the style you choose can make a big difference in how well it complements your room's design. Whether you're aiming for a traditional vibe, a modern touch, or an industrial aesthetic, there's a radiator style that can seamlessly blend with your space while delivering the necessary warmth.

Traditional Radiators
If your home boasts classic or vintage aesthetics, traditional radiators like column or cast-iron radiators are perfect for adding an old-world charm. These radiators have a timeless appeal, often found in heritage homes and period properties. Their detailed, ornate designs not only offer great heat output but also become a focal point of the room. Cast-iron radiators, in particular, retain heat for longer periods, making them efficient even after the heating is turned off. Their intricate patterns and robust build make them a standout feature in traditional homes.
Best for: Classic, vintage, or period-style homes
Why choose them? Their elegant designs are perfect for rooms with period features, and their high heat retention keeps spaces warm longer.

Modern Radiators
In contemporary homes, sleek and minimalist radiators are the way to go. Flat-panel and vertical radiators fit perfectly into modern interiors with their clean lines and unobtrusive profiles. These radiators are often engineered for maximum efficiency while taking up minimal space. Available in a range of colors and finishes, including black, white, and metallic tones, modern radiators can seamlessly integrate into living rooms, kitchens, or bathrooms. They don’t just heat your space—they also enhance the visual appeal of the room with their minimalist charm.
Best for: Modern apartments, urban homes, and sleek, streamlined interiors
Why choose them? They are unobtrusive yet stylish, offering efficient heating while blending into a contemporary design.
Industrial Style Radiators
For those who appreciate the raw, utilitarian charm of industrial-style interiors, radiators with exposed pipes or metal finishes are an excellent choice. These radiators are typically made from steel or iron, and their rugged, unfinished look complements the industrial design philosophy. Whether you choose an exposed pipe radiator, a tubular model, or a brushed steel radiator, the combination of functionality and style will give your space a bold, edgy feel. This style works exceptionally well in lofts, studios, and spaces where the raw, unrefined aesthetic of exposed elements is celebrated.
Best for: Lofts, converted warehouses, and spaces with an industrial or urban feel
Why choose them? Their raw, minimalist appeal fits perfectly with industrial decor, offering both style and efficient heating.
Radiator Materials: Selecting the Right Material for Optimal Heating and Style
When choosing a radiator, the material it’s made from plays a crucial role in its heat output, efficiency, and appearance. Different materials have distinct characteristics, each offering its own set of benefits. Let’s take a look at the most common radiator materials and how they impact your home heating and design.
1. Cast Iron Radiators
Cast iron is one of the most popular materials for traditional radiators. Known for its durability and classic charm, cast iron retains heat for long periods, even after the heating is turned off, making it highly energy-efficient. These radiators are often chosen for their vintage appeal and ability to fit into period-style homes, bringing a sense of old-world elegance. Cast iron is also effective in maintaining consistent warmth, which is ideal for larger or older rooms that require a steady, reliable heat source.
Best for: Traditional homes, vintage-style interiors, larger rooms
Why choose it? High heat retention and timeless aesthetic. Cast iron radiators offer excellent performance in terms of heat retention and distribution.
2. Steel Radiators
Steel radiators are a popular choice due to their versatility and efficiency. They come in a wide range of styles, from contemporary designs to more classic looks. Steel heats up quickly and is highly responsive to changes in temperature, making it ideal for spaces where rapid heating is needed. These radiators are typically more affordable than cast iron models, and their lighter weight makes them easier to install. Steel is also resistant to corrosion, ensuring that the radiator lasts for many years.
Best for: Modern homes, bathrooms, and smaller spaces
Why choose it? Quick heating, durability, and a wide variety of stylish designs. Steel radiators are efficient and effective in modern homes.
3. Aluminum Radiators
Aluminum is a lightweight, modern material that is known for its rapid heat-up time and energy efficiency. It heats up quickly and cools down just as fast, making it ideal for homes with a modern, high-efficiency heating system. Aluminum radiators are typically more expensive than steel but offer excellent thermal conductivity, which means they deliver heat faster and use less energy to do so. They are also resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for bathrooms or areas with high humidity.
Best for: Contemporary homes, eco-conscious buyers, and small to medium-sized rooms
Why choose it? Quick heat-up time, energy efficiency, and lightweight design. Aluminum radiators are a great choice for homeowners looking for modern, cost-effective solutions.

4. Brass Radiators
Brass radiators are a stylish and unique alternative to other radiator materials. Known for their golden hue and distinctive finish, brass radiators bring a touch of luxury and vintage flair to any space. They are often used in traditional or retro-style homes, offering both beauty and functionality. Brass is also known for its durability and resistance to rust, making it a solid choice for long-term use. However, it may require more maintenance compared to steel or aluminum due to its susceptibility to tarnishing over time.
Best for: Retro or vintage-themed rooms, high-end, traditional interiors
Why choose it? Unique, attractive appearance and long-lasting durability. Brass radiators add a touch of elegance to classic or retro interiors.
5. Copper Radiators
Copper radiators are less common but offer excellent performance due to copper’s superb heat conductivity. They heat up quickly and efficiently, providing consistent warmth throughout the room. Copper is also resistant to corrosion and can add a visually striking, modern touch to your home’s heating system. While copper radiators may be more expensive than other materials, they are highly effective and can work well in both modern and traditional settings.
Best for: Modern, industrial, or high-end design themes
Why choose it? Fast and efficient heat transfer with an eye-catching, high-end appearance. Copper radiators bring both style and superior performance.
6. Stone and Ceramic Radiators
For a more unique and eco-friendly option, stone or ceramic radiators provide an aesthetic that blends seamlessly with contemporary, minimalist, or nature-inspired interiors. These materials can store heat and release it slowly over time, creating a comfortable, balanced environment. They are typically used in energy-efficient homes or those with sustainable heating systems. Ceramic and stone radiators are also highly durable and low-maintenance.
Best for: Eco-conscious homes, modern or minimalist designs
Why choose it? Eco-friendly, energy-efficient, and aesthetically pleasing. These radiators are great for homes focused on sustainability.

Installing a Radiator: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing a radiator in your home can seem like a daunting task, but with the right tools and knowledge, it can be a straightforward process. Whether you're replacing an old radiator or adding a new one to improve your home's heating, understanding the installation process is essential. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the installation of a radiator.
Materials and Tools You’ll Need:
-
New radiator
-
Radiator valve (if not already installed)
-
Radiator brackets and wall fixings
-
Adjustable spanner
-
Pipe cutter (if necessary)
-
Teflon tape or joint sealant
-
Level
-
Drill with masonry or wood bit
-
Screwdriver
-
Bucket or towel (for draining any remaining water from the pipes)
-
Radiator bleed key
-
Pipe fittings and connectors (if needed)
Step 1: Turn Off the Heating System
Before you begin, it’s crucial to turn off your central heating system. Let the radiators cool down to prevent burns and ensure you’re not working with hot water. You may also need to shut off the water supply to the system if you plan to drain the pipes completely.
Step 2: Remove the Old Radiator (If Replacing)
If you're replacing an old radiator, you’ll need to remove it first:
-
Drain the radiator by closing the valves and opening the bleed valve to let any water out. You may need to place a bucket or towel underneath to catch any residual water.
-
Loosen the nuts and bolts connecting the radiator to the valve, and carefully remove it from the brackets.
-
If necessary, remove the old valve fittings and pipework to make room for the new installation.
Step 3: Mark and Drill Holes for the Brackets
-
Hold the new radiator in place on the wall, ensuring it's level and properly aligned with the space.
-
Mark the position for the brackets using a pencil or marker. The brackets should be installed at the points where the radiator will be supported.
-
Drill holes for the brackets using the appropriate size drill bit for your wall material (masonry, wood, or plaster). Ensure the holes are deep enough for the wall plugs and screws.
Step 4: Attach the Wall Brackets
-
Once the holes are drilled, insert wall plugs (if necessary) and secure the brackets in place with screws. Ensure they are level and tightly fixed to support the weight of the radiator.
Step 5: Install the Radiator Valves
-
If your new radiator doesn’t come with pre-installed valves, you'll need to install them now. Apply Teflon tape or joint sealant around the threaded ends of the valve to ensure a tight seal and prevent leaks.
-
Screw the valves onto the radiator, making sure they are tightly secured. Ensure the valve is positioned at the correct end of the radiator – typically, the inlet valve is on the left side, and the outlet valve is on the right.
Step 6: Connect the Radiator to the Pipes
-
With the radiator in place on the wall brackets, connect the pipes to the valves. Use appropriate pipe fittings and connectors to ensure a secure and leak-proof connection.
-
Tighten the nuts and fittings with an adjustable spanner. Be careful not to overtighten, as this can damage the threads or cause the pipes to crack.
Step 7: Fill the Radiator System
-
Once the radiator is connected, open the valves to allow water to flow into the radiator. Check the connections for any leaks as the system fills.
-
Bleed the radiator using a radiator bleed key to release any trapped air. This ensures that the radiator fills completely with water and works efficiently.
-
Turn the heating system back on and check that the radiator heats up properly. If necessary, bleed the radiator again to remove any air trapped inside.
Step 8: Check for Leaks and Test the System
-
Once the radiator is full and the system is turned on, leave it running for a while to check for leaks. Inspect the radiator, valve connections, and pipework to ensure there’s no water dripping.
-
If you detect a leak, turn off the heating system, drain the radiator, and recheck the fittings to make sure everything is tightly secured.
Step 9: Final Touches
-
If everything is working correctly and there are no leaks, you’re done! You can now use the radiator to heat your room.
-
Consider adding a radiator cover or styling the area around the radiator to complement your room’s decor.
Tips for Radiator Installation
-
Proper Sizing: Ensure that the radiator is the correct size for the room you're heating. A radiator that is too small won’t adequately heat the room, while one that is too large may lead to excessive heating and energy waste.
-
Placement: Radiators should be placed in areas where heat can circulate efficiently. Typically, installing radiators under windows or on external walls helps offset heat loss.
-
Leveling: Always use a level to ensure your radiator is installed correctly. An uneven radiator can affect the heat distribution and cause an inefficient heating system.
-
Pipework: If you’re installing a radiator in a room without existing pipework, you may need to call a professional plumber to install the necessary pipes and connectors.
-
Radiator Bleeding: If the radiator isn’t heating up evenly, it may need to be bled to remove trapped air. Always bleed radiators when you first install them and periodically throughout their life.

Maintaining and Cleaning a Radiator: Tips for Long-Lasting Efficiency
Radiators are a vital part of your home’s heating system, keeping your spaces warm and comfortable throughout the colder months. Like any appliance, they require proper care and maintenance to function efficiently and last longer. Regular cleaning and maintenance help prevent issues like blocked pipes, poor heating performance, and excessive energy consumption.
Why Is Radiator Maintenance Important?
Regular radiator maintenance is essential for several reasons:
-
Improved Efficiency: A clean radiator heats up more effectively, reducing energy waste and helping your heating system run efficiently.
-
Preventing Leaks and Blockages: Over time, debris and dust can accumulate in the radiator or its valves, affecting water flow and heat distribution.
-
Longer Lifespan: Proper care ensures that your radiator lasts longer and reduces the likelihood of needing expensive repairs or replacements.
How to Clean a Radiator
Cleaning your radiator can be a simple task, but it’s important to do it properly to avoid damaging it. Here’s how to clean your radiator effectively:
1. Turn Off the Heating System
Before starting, ensure the heating system is switched off and your radiator has cooled down. This will prevent burns and make it easier to clean without damaging the surface.
2. Remove Dust from the Surface
Using a vacuum cleaner with a soft brush attachment, gently remove any dust or debris from the surface of the radiator. Focus on the fins and the areas between the vertical metal slats, where dust and dirt tend to collect. Make sure to do this regularly, ideally once a month, to keep the radiator running efficiently.
3. Clean the Fins with a Brush
If dust has built up in the radiator’s fins, use a radiator cleaning brush or a soft, long-handled brush to dislodge and remove it. Radiator cleaning brushes are designed to fit between the fins and make it easier to clean hard-to-reach areas.
You can also use a microfiber cloth to wipe the surface and the edges of the radiator, especially if there are any stains or marks.
4. Flush the Radiator (If Necessary)
If your radiator is clogged with debris or rust, it may need to be flushed. You can do this by following these steps:
-
Turn off the radiator and let it cool.
-
Place a towel and a bucket underneath the radiator valves to catch any water that may spill.
-
Attach a hose to the drain valve (if your radiator has one) and open the valve to release the water. This will help clear out debris and ensure smooth water flow.
-
Close the valve and refill the radiator with clean water, and check for any leaks. You may need to repeat the process a few times if there’s significant buildup.
5. Bleed the Radiator
Bleeding a radiator is crucial to ensure that air trapped inside doesn’t affect its heating performance. Air pockets can prevent hot water from circulating properly, leaving some areas of the radiator cold.
Here’s how to bleed your radiator:
-
Use a radiator key to open the bleed valve at the top of the radiator. Place a small container or cloth under the valve to catch any water that may come out.
-
Once the valve is open, you’ll hear a hissing sound as the trapped air escapes. Once the water starts to flow steadily, close the valve tightly.
-
Turn the heating system back on and check for any leaks.
6. Wipe Down the Exterior
Once your radiator is clean and bled, wipe down the exterior with a damp cloth to remove any remaining dust and dirt. You can also use a mild cleaning solution (water and a small amount of dish soap) if needed. Dry the surface thoroughly to avoid rust buildup.
Radiator Maintenance Tips
Proper radiator maintenance can ensure optimal performance and extend its lifespan. Here are some essential tips:
1. Check for Leaks Regularly
Check the radiator, valves, and pipework for leaks, especially after turning on the heating system. If you notice any leaks, they should be addressed immediately to prevent further damage and water wastage.
2. Keep the Area Around the Radiator Clear
Avoid placing furniture, drapes, or other objects directly in front of the radiator, as this can obstruct airflow and reduce the radiator’s efficiency. Allow ample space for the heat to circulate.
3. Protect the Radiator’s Surface
Avoid using abrasive cleaning materials, as they can scratch and damage the surface of the radiator. Always use soft cloths, sponges, or brushes.
4. Have Your Heating System Serviced Regularly
To ensure your heating system is running efficiently, consider having a professional service the system once a year. This can prevent issues like blocked pipes, faulty valves, or damaged components that may affect radiator performance.
How Often Should You Clean Your Radiator?
The frequency of radiator cleaning will depend on your home environment:
-
Regular Cleaning: Vacuum the radiator surface monthly to remove dust and debris.
-
Deep Cleaning: Flush the radiator and bleed it once or twice a year (or more if you notice uneven heating).
-
Professional Servicing: Have your heating system professionally serviced every 1-2 years.
Cost of Radiator Maintenance in the UK
Maintaining a radiator doesn’t have to be costly, but there are some expenses involved:
-
Radiator Cleaning Brushes: Around £5-£20, depending on the size and quality.
-
Professional Radiator Bleeding: If you hire a plumber or heating engineer to bleed your radiator, it may cost between £40-£80 per hour.
-
Replacement Parts: If you need to replace any parts, such as valves or thermostatic controls, the cost can vary between £10-£50 per part.
Cost of Radiators in the UK
Radiator costs in the UK can vary widely based on factors like type, size, material, and installation. Here's a brief breakdown:
Types of Radiators and Costs:
-
Panel Radiators: £40 to £300 – Standard and affordable for most rooms.
-
Column Radiators: £80 to £800 – Traditional, elegant style, typically cast iron.
-
Towel Rails & Heated Towel Radiators: £50 to £400 – Great for bathrooms.
-
Designer Radiators: £150 to £2,000+ – Stylish and high-end.
-
Electric Radiators: £50 to £600 – Convenient and energy-efficient for small spaces.
-
Underfloor Heating: £200 to £2,000 – Popular alternative for whole-room heating.
Factors Affecting Cost:
-
Material: Steel (cheaper), Cast Iron (more expensive due to durability and style).
-
Size & BTU Rating: Larger radiators or those with higher BTU ratings cost more.
-
Brand: Well-known brands charge more for quality.
Installation Costs:
-
Simple Install: £100 to £200
-
Complex Install: £200 to £400 (for pipework or relocation)
Energy Efficiency:
Modern radiators are more energy-efficient, which helps lower your long-term energy bills.
The cost of a radiator depends on type, material, size, and installation needs. Choose based on your room’s requirements, aesthetic preferences, and budget. Regular maintenance and energy-efficient models will help reduce long-term costs.
BTU Ratings: Understanding Heat Output
When it comes to choosing the right radiator for your home, one of the most important factors to consider is the BTU (British Thermal Unit) rating. This figure indicates how much heat a radiator produces over a period of time, typically an hour. Understanding BTU ratings is essential to ensure your radiator is powerful enough to efficiently heat your space without wasting energy.
What Is a BTU?
A BTU is a measurement of energy used to quantify the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In simple terms, the higher the BTU rating of a radiator, the more heat it will provide to your room.
Why Are BTU Ratings Important?
The BTU rating helps you determine if a radiator is powerful enough for the room size you're heating. If the BTU rating is too low, your radiator will struggle to heat the space effectively, leading to cold spots and poor temperature control. On the other hand, a radiator with a high BTU rating may overheat the space, wasting energy and increasing your heating bills.
How to Choose the Right BTU Rating
To find the ideal BTU rating for your radiator, several factors must be considered, including the size of the room, its insulation quality, the number of windows, and even the room’s function (for example, kitchens and bathrooms typically require more heat than bedrooms). Here are some general steps to calculate the correct BTU:
-
Measure the Room Size:
Start by measuring the room’s length, width, and height. Multiply these dimensions to get the volume of the room in cubic feet. -
Consider Insulation and Room Features:
Poorly insulated rooms or spaces with large windows may require additional BTUs to maintain a comfortable temperature. -
Calculate the Required BTU Output:
There are online BTU calculators that can make this process easier by taking into account all these factors. Alternatively, a simple rule of thumb is to estimate around 20 BTUs per square foot of space in a typical room with average insulation.
BTU Ratings by Room Type
-
Small Room (100–150 sq ft): Around 3,000 - 5,000 BTUs
-
Medium Room (150–250 sq ft): Around 5,000 - 7,000 BTUs
-
Large Room (250–400 sq ft): Around 7,000 - 12,000 BTUs
Energy Efficiency and BTU
A radiator with the correct BTU rating helps you maintain an energy-efficient and comfortable environment. If your radiator is too powerful, it can heat the room too quickly, leading to temperature fluctuations. If it’s too weak, the radiator will work harder to maintain a warm temperature, consuming more energy.
Other Considerations
-
Radiator Placement: The location of your radiator also impacts its heating efficiency. A radiator placed near an external wall or under a large window will need to work harder to maintain heat, meaning you might need a higher BTU output for optimal performance.
-
Room Insulation: A well-insulated room retains heat better and may require fewer BTUs than a poorly insulated room, which will lose heat more quickly.

Energy Consumption by Radiators in the UK
Energy consumption by radiators in the UK can be influenced by various factors. Here's a breakdown of key points to consider:
-
Electric Radiators:
-
Wattage: The energy consumption of electric radiators is based on their wattage. The higher the wattage, the more energy it consumes. For example, a 1,000-watt electric radiator uses 1 kWh of electricity per hour.
-
Running Costs: An electric radiator typically uses between 500 to 2,000 watts. The cost of running it depends on the electricity tariff in your area.
-
Central Heating Radiators:
-
Boiler Efficiency: The efficiency of the boiler in a central heating system plays a significant role in energy consumption. Modern condensing boilers are more energy-efficient than older models.
-
Size of Radiator: The size of the radiator should match the size of the room. Oversized radiators may consume more energy than necessary, while undersized ones may run longer to heat the room.
-
Room Size and Insulation:
-
Room Size: Larger rooms require more energy to heat, so choosing the correct size radiator is important to avoid overuse of energy.
-
Insulation: Proper insulation in your home can reduce the energy needed to heat the space and make your radiator work more efficiently.
-
Thermostatic Radiators:
-
Thermostatic Control: Radiators with thermostatic valves or controls are more energy-efficient because they automatically adjust their heat output to maintain the desired room temperature, preventing excess energy use.
-
Old vs. New Systems:
-
Older Radiators: Older radiators or systems with inefficient boilers will consume more energy than newer, more efficient models.
-
Upgrading: Upgrading to an energy-efficient radiator system or modernizing your boiler can reduce overall energy consumption.
By considering these factors, you can optimize the energy consumption of your radiators and reduce heating costs.

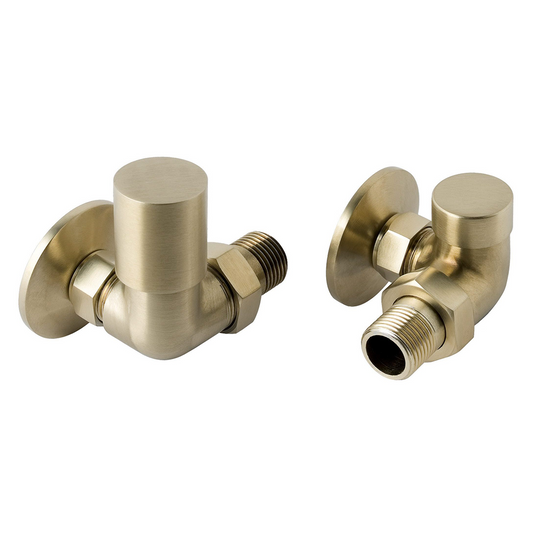
Radiator Valves: Essential Components for Efficient Heating
Radiator valves are an integral part of any heating system. These valves allow you to control the flow of hot water or steam to your radiator, giving you control over the temperature and heat output in each room. Choosing the right radiator valves is crucial to ensure that your heating system is both efficient and responsive to your needs.
Types of Radiator Valves:
-
Thermostatic Radiator Valves (TRVs):
-
Function: TRVs are designed to automatically adjust the flow of water through the radiator based on the room temperature. They help maintain a comfortable temperature by regulating heat output.
-
Benefits: TRVs can save energy by only heating the room to the desired temperature and preventing overheating. This makes them ideal for rooms with varying heating needs.
-
Where to Use: TRVs are best used in bedrooms, living rooms, and other areas where temperature control is important.
-
Manual Radiator Valves:
-
Function: Manual valves require you to adjust the flow of water manually. You open or close the valve to control the heat output.
-
Benefits: These are simpler and generally more affordable than TRVs, but they require constant attention to adjust the temperature.
-
Where to Use: Ideal for areas where temperature control is less critical or where you don't mind manually adjusting the radiator.
-
Lockshield Valves:
-
Function: Lockshield valves are used in conjunction with the manual or TRV to regulate water flow and balance the system. They are usually located at the opposite end of the radiator.
-
Benefits: Lockshield valves help balance the heating system by adjusting the flow of water to individual radiators, ensuring an even distribution of heat throughout the house.
-
Where to Use: Typically used in central heating systems to ensure that all radiators receive the appropriate water flow.
-
Angle Valves:
-
Function: These valves are designed to connect the radiator to the supply pipe at an angle, often used when the pipework is angled or when space constraints require it.
-
Benefits: Angle valves provide a neat and space-efficient solution for installing radiators in tight or awkward spaces.
-
Where to Use: Ideal for installations where the radiator pipes need to be bent or when space is limited.
-
Straight Valves:
-
Function: Straight valves connect the radiator directly to the supply pipe without any angle.
-
Benefits: They are the most straightforward valve type, providing a direct connection to the pipework.
-
Where to Use: Used in situations where the pipework runs in a straight line to the radiator.
Choosing the Right Radiator Valve:
-
Compatibility: Ensure the valve is compatible with the radiator type and the pipework configuration.
-
Design: Consider the design of the valve, as there are modern and traditional styles that can complement your radiator and room design.
-
Size: Make sure the valve size matches the radiator and piping size for optimal performance.
-
Ease of Use: If ease of use is a priority, thermostatic valves provide automatic control, while manual valves offer more direct control.
Radiator valves are essential for controlling the temperature and efficiency of your home’s heating system. Choosing the right valve depends on your preferences for temperature control, ease of use, and the design of your radiator. Whether you go for thermostatic, manual, or lockshield valves, each offers distinct benefits that can enhance your heating experience.
Essential Accessories and Considerations for Radiator Installation and Maintenance
When it comes to purchasing and setting up radiators, there are a variety of accessories and additional features to consider that can improve both the functionality and aesthetics of your heating system. These accessories not only help in maintaining your radiators but also enhance the efficiency and overall look of your space. Here are some important accessories and considerations:
-
Radiator Covers:
Radiator covers are an excellent choice if you want to enhance the look of your radiator while also protecting it from dust, dirt, and damage. They come in various designs, from traditional wooden covers to more modern, sleek options made from metal or plastic. Not only do they help in improving the appearance of your radiator, but they can also be a safety feature, especially in homes with children or pets. Some radiator covers even help distribute heat more evenly across the room. -
Radiator Bleeding Key:
A radiator bleeding key is a small, essential tool for releasing air that can become trapped inside your radiator. Air in the radiator can prevent the efficient circulation of hot water, leading to cold spots and reduced heating performance. Bleeding your radiator periodically ensures that it operates at its best, helping to maintain even heat distribution and prevent unnecessary strain on the system. The key is easy to use and usually comes with a valve located at the top of the radiator. By using the key to open the valve slightly, you can release the trapped air and restore optimal heating efficiency. -
Wall Brackets:
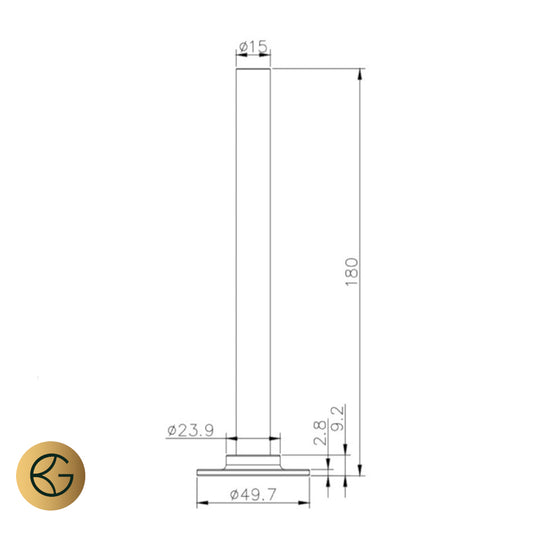
Wall brackets are necessary for securely mounting the radiator onto the wall, especially for wall-mounted or vertical radiators. These brackets ensure that the radiator is fixed firmly in place, which not only helps with stability but also ensures that it is positioned for maximum heat efficiency. The right placement of the radiator can help with air circulation in the room, ensuring that the heat is distributed effectively. When installing a radiator, it’s crucial to use the correct wall brackets that are compatible with your radiator’s size and design.
These accessories contribute to the proper installation, functionality, and longevity of your radiator, ensuring a comfortable and efficient heating system for your home.
Buying Tips for Choosing the Right Radiator
When selecting the right radiator for your home, consider these essential factors:
-
Size and Heating Requirements: Calculate the required BTU based on room size, insulation, and layout for efficient heating.
-
Material: Choose between steel, cast iron, or aluminum based on your home’s style and heating needs.
-
Radiator Style: Pick a style that complements your decor—traditional column, modern flat-panel, or vertical for small spaces.
-
Energy Efficiency: Opt for thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs) or smart radiators for better control and energy savings.
-
Space & Placement: Ensure the radiator fits the space without blocking doors or windows and suits the room’s layout.
-
Budget: Balance quality and price, and factor in installation costs for a long-lasting, functional solution.
-
Maintenance: Choose easy-to-clean designs, and remember to bleed the radiator regularly to maintain efficiency.
By evaluating these factors, you can find the perfect radiator to keep your home warm and stylish while maintaining energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the right radiator involves balancing functionality with aesthetics. Whether you need a practical panel radiator, a stylish column model, or a modern designer radiator, there’s a perfect fit for every home. By considering the type, size, materials, and energy efficiency, you’ll be able to select the best radiator for your space, ensuring comfort and style for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
You can calculate the necessary BTU rating for your room using online calculators, which consider room size, insulation, and the desired temperature.
A TRV automatically adjusts the flow of water into the radiator based on the room's temperature, helping maintain a consistent temperature and improve energy efficiency.
Yes, electric radiators typically cost more to run compared to water-powered radiators, especially when used to heat an entire home.
While some small radiators can be installed by DIY enthusiasts, it’s recommended to hire a professional plumber or heating engineer for optimal installation and to avoid any issues.
Radiators should be cleaned at least once a year, and you should bleed them regularly to ensure proper heat distribution.