How and why to bleed a radiator ( Easy Guide )
Table Of Contents:
-
Transform Your Heating Efficiency: Simple Steps to Bleed Your Radiator Explained
→ -
Gold Towel Radiators Collection
→ -
Definition of Bleeding a Radiator
→ -
Signs You Need to Bleed a Radiator
→ -
Tools Required
→ -
Steps to Bleed a Radiator
→ -
Radiator Bleeding Tips
→ -
Special Cases
→ -
Frequency of Bleeding
→ -
Common Issues Beyond Air Trapped
→ -
Energy Efficiency and Cost Saving
→ -
Boiler Manual and Pressure
→ -
Auto-Bleed Valves
→ -
Conclusion
→ -
Frequently Asked Questions
→
Transform Your Heating Efficiency: Simple Steps to Bleed Your Radiator Explained
Welcome to our easy guide on bleeding a radiator—your key to maintaining a warm, efficient home! Our guide stands out by offering clear, step-by-step instructions tailored for both DIY enthusiasts and novices alike. In this blog, you'll learn how to quickly and effectively release trapped air from your radiators, a crucial task for ensuring even heat distribution and optimizing your central heating system. You’ll be excited to discover practical tips on using common tools and troubleshooting special cases, plus insights into how proper radiator maintenance can save you money on your heating bills.
Definition of Bleeding a Radiator
Bleeding a Radiator involves releasing trapped air from inside the radiator to ensure it heats efficiently and uniformly. When a central heating system is initially filled or after it has been inactive for some time, air can become trapped within the radiator. This trapped air creates bubbles that disrupt the flow of hot water through the radiator, resulting in uneven heating. The process of bleeding involves using a special tool to open a small valve on the radiator, allowing the trapped air to escape until a steady flow of hot water is observed. This action restores proper water circulation within the radiator, improving its performance and heat distribution. Bleeding a radiator is a simple but essential maintenance task to ensure that the heating system operates at peak efficiency and provides consistent warmth throughout your home.
Signs You Need to Bleed a Radiator
Cold Spots at the Top: One of the most common signs that a radiator needs bleeding is when the top portion of the radiator remains cold while the bottom is warm. This occurs because the trapped air at the top of the radiator prevents hot water from reaching that area. As a result, the radiator fails to heat uniformly, leaving cold patches at the top. If you notice that only part of your radiator is getting warm, it is likely that air is trapped and needs to be released to restore even heating.
Noises: Radiators can produce various noises when air is trapped inside them. Common sounds include clunking, banging, or gurgling. These noises occur as air bubbles move around within the water or when air is being forced through the radiator. These disruptive sounds are especially noticeable when the heating system first starts up or while it is running. The presence of these noises typically indicates that the air in the radiator is causing turbulence and needs to be expelled to ensure smooth operation.
Slow Heating: If your radiator is taking longer than usual to heat up or is not reaching the desired temperature, it could be a sign that it needs bleeding. Trapped air obstructs the flow of hot water through the radiator, making it less effective at warming up. This inefficiency can lead to extended heating times and reduced overall performance.
Tools Required
Radiator Bleed Key: The radiator bleed key is a small, specially designed tool used to open the bleed valve on a radiator. It is typically square or slotted and fits precisely into the valve to release trapped air. This key is essential for the bleeding process, and most hardware stores carry them.
Flathead Screwdriver: In the absence of a radiator bleed key, a flathead screwdriver can be used as an alternative. It can fit into the slot of the bleed valve, although this is not ideal and may not provide as secure a fit as a proper bleed key. This tool is used to turn the valve and allow air to escape.
Cloth or Towel: A cloth or towel is placed under the bleed valve to catch any water that might drip out during the process. This prevents water from making a mess on the floor and helps keep the area clean. It’s important to use a cloth or towel to manage any spillage that occurs when the valve is opened.
Container or Tray: A container or tray is used to collect excess water that may escape from the radiator when bleeding. This helps in managing the water and prevents it from spilling onto the floor, which can cause water damage or create a slipping hazard.
Steps to Bleed a Radiator
Turn Off the Heating and Wait for the System to Cool: It’s crucial to turn off the heating system and let the radiator cool down before you start bleeding. This prevents hot water from escaping, which can cause burns and ensure that the air trapped in the radiator is released in a controlled manner. Allowing the system to cool also ensures that you handle the radiator safely.
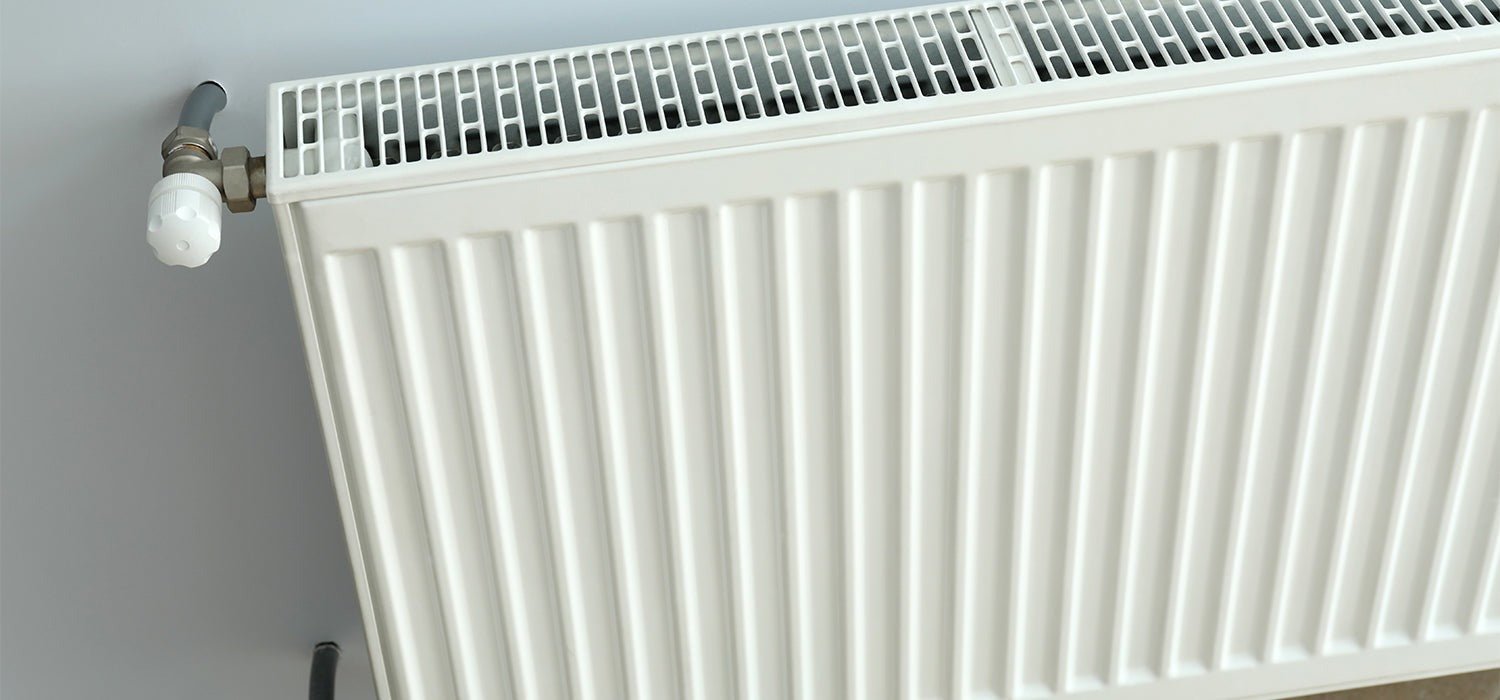
Locate the Bleed Valve: The bleed valve is typically located at the top of the radiator, often on one side. It’s a small valve that can be either round with a square or slot-shaped opening. Locating this valve is the first step in the bleeding process. If you’re unsure where it is, consult your radiator’s manual or look for a small screw-like fitting.
Prepare the Area: Before opening the valve, place a cloth or towel under it to catch any water that might escape. Position a container or tray underneath the cloth to catch the water and prevent it from making a mess. This preparation helps manage the drips and keeps your working area clean.
Insert and Turn the Bleed Key: Insert the radiator bleed key into the valve and turn it slowly anti-clockwise. You should hear a hissing sound as air escapes. This is normal and indicates that the air is being released. Continue turning until you see a steady flow of water, which means that the air has been fully expelled.
Wait for Steady Water Flow: Once you start seeing water flowing steadily from the valve without air bubbles, it’s time to close the valve. This steady flow signifies that all the trapped air has been released and that the radiator is now filled with hot water. Turn the bleed key clockwise to close the valve securely.
Turn Heating Back On and Check Radiator Performance: After closing the valve, turn your heating system back on. Check the radiator to ensure it heats up properly and evenly. Monitor its performance over the next few hours to confirm that it’s functioning as expected.
Radiator Bleeding Tips
Start with the Radiator Furthest from the Boiler: Bleeding the radiator furthest from the boiler first ensures that air is removed from the entire system in a systematic manner. This is crucial because the radiator closest to the boiler will often have the least amount of trapped air. When you bleed the radiator furthest from the boiler, it helps push the air trapped in the system towards the end of the line. This practice helps to remove air pockets effectively, ensuring that all radiators receive consistent hot water. If you start with the nearest radiator, you might leave air trapped in the system, which can cause inefficient heating and uneven temperature distribution.
Avoid Over-Tightening the Bleed Valve: After you have bled the radiator and the air has been released, it’s important to close the bleed valve properly but not excessively. Over-tightening can damage the valve’s threads or the radiator itself. If the valve is over-tightened, it may become difficult to open in the future, and the stress can lead to leaks. A properly closed valve should be snug but not forced. If you’re unsure, turn the valve until it’s just tight enough to stop any water from leaking, but no more. This balance ensures longevity and proper functionality of the valve and radiator.
For Multiple Radiators, Bleed in Order: When you have multiple radiators, bleeding them in the correct sequence—starting with the one furthest from the boiler and working towards the closest—ensures that air is expelled effectively. This method prevents air from becoming trapped in the system and ensures that hot water flows evenly through all radiators. If you bleed the radiators out of order, air pockets can remain in the system, leading to inefficient heating and cold spots. By following this sequence, you facilitate a smoother and more efficient heating process.
Handle the Valve Gently: When operating the bleed valve, apply gentle and controlled pressure. The bleed valve is a delicate component, and excessive force can damage the valve or its housing, leading to potential leaks or malfunctions. Use a radiator key or a flathead screwdriver carefully, turning the valve slowly counter-clockwise to release air. If the valve resists, don’t force it—apply gentle pressure and consider using a penetrating oil if necessary. This careful handling helps maintain the integrity of the valve and ensures it operates correctly.
Special Cases
Towel Radiators: Towel radiators often have different designs and types of bleed valves compared to standard radiators. They might use a different tool or have a unique mechanism for bleeding. Ensure you use the appropriate tool or method for your towel radiator to avoid damaging it. If you’re unsure about the type of valve or tool needed, consult the manufacturer’s instructions or seek advice from a professional. Proper bleeding of towel radiators is essential for their efficient operation and to ensure they provide adequate heat.
Stuck Valve: If the bleed valve is stuck and won’t turn, try using gentle pressure or a penetrating oil to loosen it. Apply the oil sparingly and allow it to sit for a few minutes to help break down any rust or debris causing the valve to stick. Avoid using excessive force, as this can damage the valve or radiator. If the valve remains stuck after attempting these methods, you may need to seek professional assistance to avoid further damage.

Leaking Valve: If you notice that the bleed valve is leaking after you’ve completed the bleeding process, it may be due to improper tightening or a faulty valve. First, check if tightening the valve slightly more stops the leak. If the leak persists, you might need to replace the valve or seek professional help. Leaking valves can affect the efficiency of your heating system and may lead to water damage if not addressed promptly.
Combi Boilers: For systems with combi boilers, it's important to check and adjust the boiler pressure after bleeding the radiators. Bleeding radiators can cause a drop in system pressure, so you may need to top up the pressure to maintain optimal performance. Refer to your boiler manual for specific instructions on adjusting the pressure, and use the boiler pressure gauge to ensure it remains within the recommended range (typically between 1 and 1.5 bars). Maintaining proper pressure is crucial for the effective operation of your heating system and to prevent issues like insufficient heating or system errors.
Frequency of Bleeding
Regular Maintenance Schedule: Bleeding your radiators on a regular schedule, ideally once a year at the start of the heating season, ensures that trapped air is removed before the system is put under heavy use. This annual maintenance helps to prevent common issues associated with air pockets, such as uneven heating or reduced efficiency. By addressing air pockets early, you ensure that the radiators operate at peak efficiency throughout the colder months. This preemptive step is crucial in maintaining the system’s performance and avoiding potential problems that could arise from neglected air trapped within the radiators.
Periodic Checks During Winter: During the winter months, it’s beneficial to periodically check your radiators for any signs of inefficiency. As the heating system is in constant use, air bubbles can accumulate, or new issues may surface. Observing symptoms like uneven heating, unusual noises, or cold spots can indicate that the radiators need attention. In such cases, bleeding the radiators can help restore optimal performance. Regular checks and timely maintenance during the winter ensure that the heating system remains effective, providing consistent warmth and comfort while potentially reducing heating costs by preventing inefficiencies.
Common Issues Beyond Air Trapped
Sludge Build-Up: If bleeding a radiator does not resolve heating issues, sludge build-up might be the problem. Sludge consists of rust, limescale, and other debris that accumulates over time, typically settling at the bottom of radiators. This build-up obstructs water flow and can cause cold spots or uneven heating. To address this issue, a system flush may be necessary. Flushing the system involves circulating a cleaning solution through the radiators and pipes to remove sludge and restore proper circulation. Regularly scheduled system flushes can prevent sludge accumulation and ensure consistent radiator performance.
System Flushing: When bleeding the radiators doesn’t fix persistent heating problems, it may be necessary to perform a system flush. A system flush involves introducing a cleaning agent into the central heating system, which is then circulated to dissolve and remove accumulated sludge, rust, and debris. This process helps to clear blockages and restore the efficient flow of water through the radiators. Flushing is particularly important if sludge build-up is causing significant cold spots or reduced efficiency. Professional flushing services are often recommended to ensure thorough cleaning and to address any underlying issues that may be affecting the heating system.
Checking for Leaks: Persistent issues with radiator performance, even after proper bleeding, could indicate leaks within the heating system. Leaks can cause reduced system pressure, resulting in inefficiencies and potential damage to the system. Common signs of leaks include water stains, pooling water, or damp patches around the radiator. If leaks are suspected, it’s important to inspect the system thoroughly and address any issues promptly. Small leaks can sometimes be fixed with tightening connections or seals, but more significant leaks may require professional repair. Regularly checking for leaks helps maintain the system’s efficiency and prevents further damage.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Saving
Optimizing Energy Use: Properly bled radiators function more efficiently, allowing hot water to circulate evenly and effectively throughout the radiator. This improved circulation ensures that the radiator heats up evenly and quickly, reducing the amount of energy required to reach the desired temperature. Efficient radiators help maintain consistent room temperatures with less effort from the heating system. By eliminating air pockets and ensuring optimal radiator performance, you can reduce energy consumption, as the system does not have to work harder to compensate for inefficiencies, ultimately leading to lower energy bills and better overall system performance.
Reducing Heating Costs: Maintaining properly functioning radiators through regular bleeding and maintenance contributes to reduced heating costs. Efficient radiators heat rooms more effectively, allowing for better temperature control and less reliance on the heating system. This efficiency translates to shorter operating times and reduced energy consumption, which helps lower your heating bills. Additionally, by addressing issues like trapped air or sludge build-up, you prevent the system from running inefficiently, further contributing to cost savings. Investing in regular radiator maintenance and prompt repairs can lead to long-term financial benefits and a more cost-effective heating solution.
Boiler Manual and Pressure
Consulting the Manual: Always refer to your boiler’s manual for specific guidance on maintaining and adjusting system pressure. The manual provides detailed information on the correct pressure range for your particular boiler model, typically between 1 and 1.5 bars. Following these guidelines is crucial for ensuring the boiler operates efficiently and safely. The manual will also offer instructions on how to adjust the pressure if it falls outside the recommended range. Regularly consulting the manual helps you stay informed about your boiler’s requirements, preventing potential issues related to incorrect pressure and ensuring optimal heating system performance.
Maintaining Pressure: Maintaining the correct pressure in your heating system is essential for efficient operation. The pressure should generally be between 1 and 1.5 bars, as specified by most boiler manufacturers. Low pressure can lead to reduced heating efficiency and can cause the system to fail to heat properly. On the other hand, excessively high pressure can strain the system and potentially cause damage. Regularly check the pressure gauge on your boiler and adjust as necessary according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Keeping the pressure within the recommended range ensures that the heating system operates smoothly and effectively, providing consistent warmth throughout your home.
Auto-Bleed Valves
Convenience of Auto-Bleed Valves: Auto-bleed valves are designed to automatically release trapped air from radiators without the need for manual intervention. These valves offer a convenient solution for maintaining radiator efficiency by continuously expelling air that accumulates over time. Auto-bleed valves help prevent common issues associated with trapped air, such as uneven heating and reduced radiator performance. By eliminating the need for regular manual bleeding, these valves simplify radiator maintenance and ensure that the heating system operates at optimal efficiency. Installing auto-bleed valves can enhance the convenience of radiator upkeep and contribute to long-term system performance.
Installation and Benefits: Installing auto-bleed valves can greatly reduce the need for manual radiator maintenance. These valves are particularly useful for homeowners who want to minimize the hassle of periodic bleeding. Auto-bleed valves work by automatically releasing air that builds up in the radiator, maintaining efficient heat distribution and preventing common issues caused by trapped air. In addition to saving time and effort, these valves help keep the heating system running smoothly and efficiently. By integrating auto-bleed valves into your heating system, you can enjoy consistent radiator performance and potentially reduce heating costs over time.
Conclusion
Bleeding your radiator is a simple yet crucial task for maintaining an efficient and comfortable heating system. By releasing trapped air, you ensure that your radiator heats evenly, avoids annoying noises, and keeps your home cozy and warm. Remember, if you encounter persistent issues despite bleeding, such as cold spots or unusual noises, it might be time to check for sludge build-up or consult a professional for further help.
Frequently Asked Questions
If the bleed valve is stuck, gently apply pressure or use a penetrating oil to help loosen it. For a leaking valve, try tightening it slightly more. If the leak persists, you might need to consult a professional plumber to address the issue. Handle the valve carefully to avoid causing damage.
It’s best to bleed radiators one at a time, starting with the radiator furthest from the boiler and working towards the closest. This approach helps remove trapped air systematically from the entire system, ensuring even and effective heating throughout.
If bleeding the radiator does not resolve the issue, there may be other underlying problems such as sludge build-up or leaks. In such cases, a system flush might be necessary to remove accumulated sludge. If problems persist, consult a heating professional for a thorough diagnosis.
Bleeding radiators improves heating efficiency by ensuring that hot water circulates properly, which helps eliminate cold spots and reduce energy consumption. This can lead to lower heating costs and a more comfortable environment. Regularly bleeding radiators helps maintain optimal system performance and prolongs the life of your heating system.
If your radiator doesn’t have a traditional bleed valve, you might need to use alternative methods. For older radiators or towel radiators with no accessible valve, you can use a flathead screwdriver to gently loosen any fittings or connections that may be trapping air. Another option is to consult the radiator's manufacturer for specific instructions or consider professional assistance if the air-trapping issue persists.
It is best to bleed radiators when they are cold. Allowing the radiator to cool down before bleeding helps prevent hot water from spraying out and allows any trapped air to escape more easily. Additionally, bleeding radiators while they are cold minimizes the risk of burns and makes the process more manageable.
To ensure that you’ve bled your radiators properly, check if the radiator heats up evenly from top to bottom without any cold spots. After bleeding, the radiator should become warm to the touch across its entire surface. If you still notice cold spots or unusual noises, you may need to bleed the radiator again or check for other issues such as air trapped elsewhere in the system.
If your radiator is not heating properly, it might not necessarily be broken. Often, issues like uneven heating or cold spots are due to trapped air, which can be resolved by bleeding the radiator. However, if bleeding does not resolve the problem, the radiator might have other issues such as internal blockages, leaks, or corrosion. In such cases, a thorough inspection by a professional may be necessary to determine the exact problem and appropriate solution.